Division of Medical Sciences 2026: A Complete Guide

The division of medical sciences focuses on understanding human health, disease, and treatment at a scientific and clinical level. It combines knowledge from biology, chemistry, and medicine to train professionals in diagnosis, treatment, and research. This division prepares students for careers in hospitals, labs, research centers, and public health organizations, ensuring patients receive safe, effective, and evidence-based care. It is essential for building a strong, knowledgeable healthcare workforce worldwide.
Table of Contents
What Is the Division of Medical Sciences?
The division of medical sciences is a field of study that explores the structure, function, and disorders of the human body. Unlike general health sciences, it emphasizes disease mechanisms, clinical treatment, and laboratory research.
This division is organized into various specialized branches, each focusing on a distinct aspect of medicine. It exists mainly in universities, medical schools, and research institutions, aiming to produce skilled professionals who understand both the science and practice of medicine.
Key components include:
- Human anatomy and physiology
- Disease mechanisms and pathology
- Diagnostic and therapeutic procedures
- Clinical and laboratory research
- Pharmaceutical sciences
The division acts as a bridge between pure scientific research and practical patient care.
Major Branches in the Division of Medical Sciences
The division of medical sciences comprises several important branches. Each plays a unique role in understanding and treating diseases.
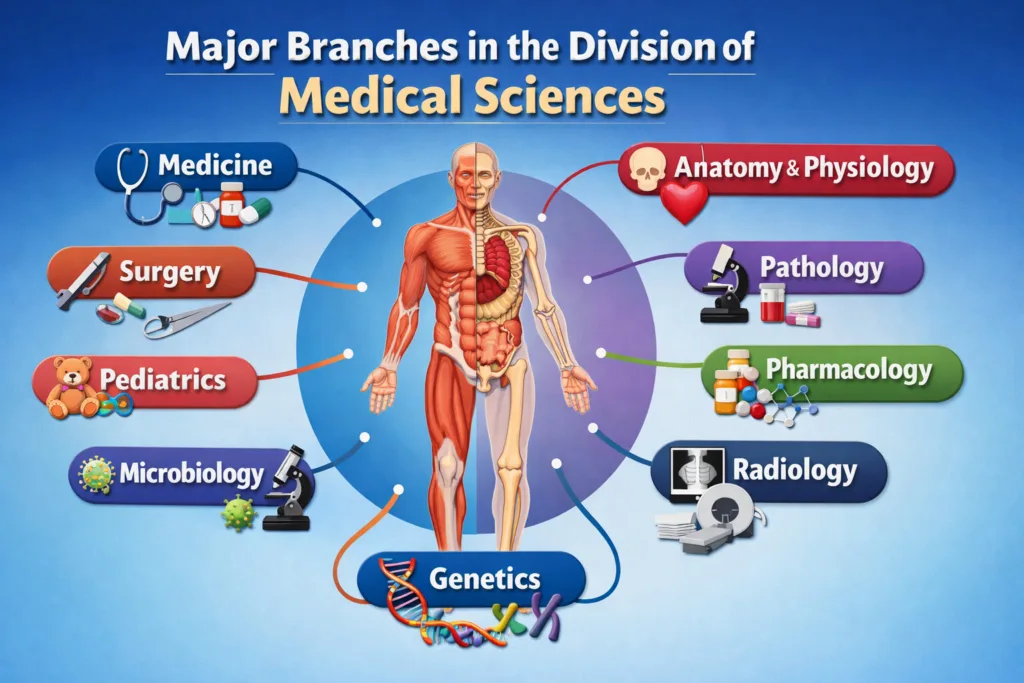
Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy studies the structure of the human body, while physiology explains how organs and systems function. This foundation is critical for understanding disease processes and treatment.
Students learn:
- Organ systems and functions
- Tissue structure and cellular processes
- Human development and genetics
Career roles include clinical anatomist, medical educator, and research assistant.
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Biochemistry studies chemical processes in the human body. Molecular biology focuses on genes, proteins, and cellular mechanisms.
Applications include:
- Understanding disease at the molecular level
- Developing targeted therapies
- Diagnosing genetic disorders
Careers: molecular biologist, clinical biochemist, pharmaceutical researcher.
Pharmacology
Pharmacology focuses on drugs and their effects on the body. It combines chemistry, biology, and medicine to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Pharmacology involves:
- Drug development and testing
- Clinical trials
- Patient medication management
Graduates can work as clinical pharmacologists, pharmaceutical researchers, or hospital pharmacists.
Pathology
Pathology studies the causes, effects, and progression of diseases. Pathologists analyze tissue, blood, and body fluids to provide accurate diagnoses.
Pathology includes:
- Histopathology
- Cytology
- Clinical pathology
- Forensic pathology
Career roles: pathologist, lab director, medical examiner.
Microbiology and Immunology
Microbiology studies microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Immunology focuses on the body’s defense mechanisms against diseases.
This field is vital for:
- Infectious disease control
- Vaccine development
- Public health management
Graduates can become microbiologists, immunologists, or infectious disease specialists.
Forensic Medicine
Forensic medicine applies medical knowledge to legal and criminal investigations. It involves analyzing injuries, cause of death, and toxicology reports.
Career paths include:
- Forensic pathologist
- Medical examiner
- Toxicologist
This branch links medicine, law, and public safety.
Academic Programs and Training
The division of medical sciences offers structured education programs at multiple levels.
Undergraduate Programs
Undergraduate programs build foundational knowledge in biology, chemistry, and clinical sciences.
Common degrees:
- Bachelor of Medicine
- BSc Medical Sciences
- Bachelor of Biomedical Science
Graduate and Postgraduate Programs
Graduate programs offer specialization in areas like pharmacology, pathology, or molecular biology.
Examples:
- MSc Medical Sciences
- Master of Pharmacology
- MPH in Medical Research
Specialization and Research Opportunities
Postgraduate studies focus on research, innovation, and advanced clinical skills. Many students pursue PhDs or MD programs to contribute to scientific knowledge or medical practice.
Importance of the Division of Medical Sciences
The division of medical sciences is essential because it ensures the scientific foundation of healthcare.
Benefits include:
- Accurate disease diagnosis
- Development of new treatments
- Evidence-based clinical practices
- Public health improvement
It is the backbone of modern medicine, integrating science and patient care.
Skills Students Acquire in Medical Sciences
Students gain both technical and soft skills, making them versatile professionals.
Key skills:
- Laboratory and clinical expertise
- Analytical and research skills
- Problem-solving and critical thinking
- Ethical decision-making
- Communication with patients and teams
These skills are applicable in hospitals, research labs, and public health organizations.
Career Opportunities After Medical Sciences
Graduates from the division of medical sciences have broad career options:
- Clinical researcher
- Pathologist or lab technologist
- Pharmacologist or pharmaceutical scientist
- Forensic medical officer
- Health policy advisor
These roles offer stability, global opportunities, and a chance to improve human health.
Role of Research and Innovation
Research is central to medical sciences. It leads to new treatments, vaccines, and diagnostic techniques.
Focus areas include:
- Clinical trials
- Gene therapy research
- Disease prevention studies
- Drug development and testing
Innovation ensures medicine continues to evolve with modern challenges.
Admission Requirements and Eligibility Criteria
Admission criteria vary but often include:
- Science background (biology, chemistry, physics)
- Minimum grades or GPA
- Entrance tests or interviews
- Clinical or research experience for advanced programs
Institutions may also require letters of recommendation or personal statements.
Difference Between Medical Sciences and Health Sciences
| Medical Sciences | Health Sciences |
| Focus on disease diagnosis and treatment | Focus on prevention, wellness, and support roles |
| Includes clinical labs and pharmacology | Includes nursing, public health, nutrition |
| Advanced scientific research required | Practical care and preventive measures |
| Often leads to doctor-related careers | Leads to allied health professions |
Both are interrelated but serve different purposes in healthcare.
Global Demand and Future Scope
Medical sciences are growing due to:
- Aging populations
- Rising chronic diseases
- Global pandemics
- Advances in biotechnology and precision medicine
Careers are in high demand worldwide, and graduates often work in research, hospitals, and policy development.
Common Challenges in Studying Medical Sciences
Challenges include:
- Intensive coursework
- Long hours in labs or clinical settings
- Stressful research deadlines
- Emotional stress from patient care
Proper time management, mentorship, and self-care are crucial for success.
Why Choose a Career in Medical Sciences?
A career in medical sciences is ideal for those passionate about science and healthcare.
Benefits:
- Meaningful contribution to patient care
- High career stability
- Global job opportunities
- Continuous learning and research
It is a field that combines curiosity, compassion, and scientific rigor.
Final Thoughts
The division of medical sciences is a cornerstone of modern healthcare. It trains professionals who diagnose diseases, develop treatments, and conduct life-saving research. With diverse programs, global opportunities, and impactful careers, it offers both professional growth and personal satisfaction. Medical sciences continue to evolve, making it a crucial and future-ready field for students worldwide.

